[ 자료구조 ] linked list 노드 삭제, 연결 리스트를 이용한 스택 큐 구현
노드 삭제
- ptr : 리스트 첫 노드를 가리키는 포인터 변수
- node : 삭제될 노드를 가리키는 변수
- trail : 삭제될 노드의 바로 앞 노드를 가리키는 변수
삭제될 노드가 첫 노드일 경우
- 삭제 후 ptr의 값이 바뀐다. 따라서 ptr의 포인터 변수로 주소를 받아 ptr의 값을 변경해야 한다.

void delete(list_ptr * ptr, list_ptr trail, list_ptr node)
{
if(node==*ptr)
*ptr = node->link;
else
trail->link = node->link;
free(node);
}
// 리스트의 첫 노드, 삭제될 노드의 앞 노드, 삭제될 노드
void delete(list_ptr * p, list_ptr before, list_ptr temp)
{
if(temp == *p) // 삭제될 노드가 리스트의 첫 노드일때
*p = temp->link; // 첫번째 노드의 값을 삭제될 노드의 링크로 바꾼다.
else // 삭제될 노드가 리스트의 첫 노드가 아닐때
before->link = temp->link; // 삭제될 앞 노드의 링크값을 현재 링크로 바꾼다.
free(node);
}
삭제될 노드가 첫 노드가 아닐 경우
- 그 외의 경우 리스트 시작 포인터인 ptr의 값이 안 바뀐다.

연결 리스트를 이용한 스택 구현
스택에서 삽입과 삭제를 하는 경우 맨 앞이나 맨뒤에서 삽입 삭제를 해야 한다.
하지만 맨뒤에서 삽입 삭제를 하는 것은 효율적이지 않기 때문에 맨 앞(top)에서 삽입, 삭제를 한다.
스택 연결 리스트는 필요한 만큼 top에 동적 할당해 사용하는 것을 기본으로 한다.
top에서 동적 할당, 삽입, 삭제를 하는 이유는 맨 앞에서 변화가 일어나기 때문이다.
스택 연결 리스트를 구현할 때는 node 대신 stack을 선언한다.
top 변수는 stack_ptr 타입으로 구현한다.
삭제는 다음 것을 가리킨다 : delete first
삽입은 맨 앞에서 한다 : insert first
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MAX_STACK_SIZE 100
struct node {
int item;
struct node *link;
};
typedef struct node stacknode;
typedef stacknode *stacknode_ptr;
stacknode_ptr top=NULL;
void push(int data) {
stacknode_ptr temp =
(stacknode_ptr)malloc(sizeof (stacknode));
if( !temp) {
fprintf(stderr,"The memory is full\n");
exit(1);
}
temp->item=data;
temp->link=top;
top = temp;
}
int pop() {
stacknode_ptr temp = top;
int item;
if( !temp ) {
fprintf(stderr,"The stack is empty\n");
exit(1);
}
item=temp->item;
top=temp->link;
free(temp);
return item;
}
int isempty()
{ if( top == NULL ) return(1); else return(0); }
int main()
{
int e;
push(20);
push(40);
push(60);
printf(" Begin Stack Test ...\n");
while(!isempty())
{
e = pop();
printf("value = %d\n", e);
}
}
#define MAX_STACKS 10
typedef struct stack *stack_ptr;
typedef struct stack{
int item;
stack_ptr link;
};
stack_ptr top;
void push(stack_ptr *top, int data){
stack_ptr temp = (stack_ptr)malloc(sizeof(stack));
if(!temp){
fprintf(stderr, "The meomory is full\n");
exit(1);
}
temp->item = item;
temp->link = *top;
*top = temp;
}
int pop(stack_ptr * top){
stack_ptr temp = *top;
int data;
if(!temp){
fprintf(stderr, "The stack is empty\n");
exit(1);
}
data = temp->item;
*top = tmep->link;
free(temp);
return data;
}
int main(){
int e;
push(20);
push(40);
push(40);
push(40);
push(60);
printf(" Begin Stack Test ...\n");
while(!isempty()){
e = pop();
printf("value = %d\n", e);
}
}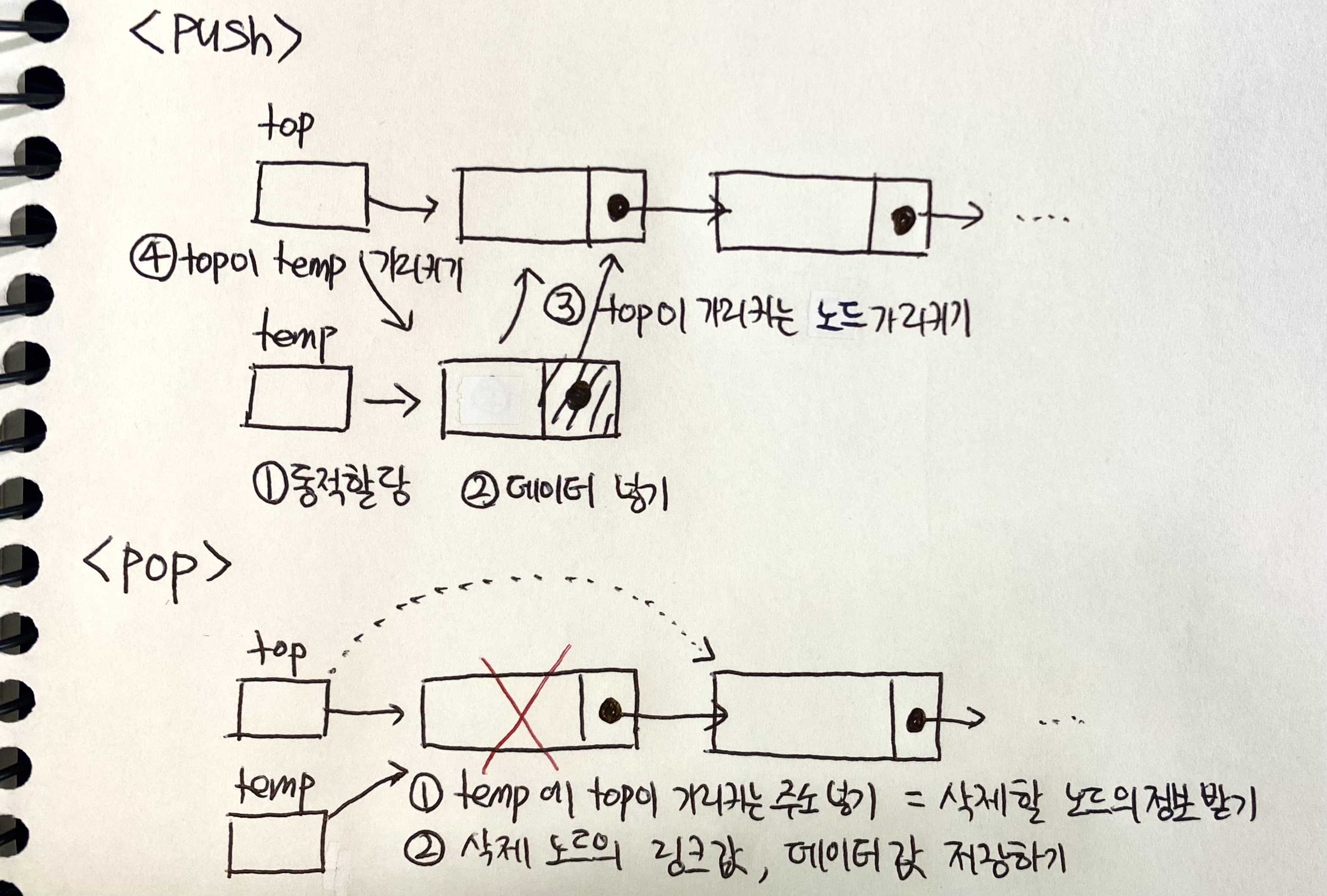
<push>
1. temp 동적 할당
2. temp가 가리키는 곳에 데이터 대입
3. temp의 link가 top이 가리키는 노드를 가리키기
4. top이 temp를 가리키도록 하기
<pop>
1. temp에 top이 가리키는 주소 넣기 = 삭제할 노드의 정보를 받기
2. 삭제 노드의 링크 값, 데이터 값 저장하기
연결 리스트를 이용한 큐 구현
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MAX_QUEUES 10 /* m=MAX_QUEUES=10 */
typedef struct {
int key;/* other fields */
} element;
struct node {
element item;
struct node* link;
};
typedef struct node queuenode;
typedef queuenode* queuenode_ptr;
void insertq(queuenode_ptr *front, queuenode_ptr *rear, element x) {
queuenode_ptr temp = (queuenode_ptr)malloc(sizeof(queuenode));
if( !temp ) {
fprintf(stderr,"The memory is full\n");
exit(1);
}
temp->item=x;
temp->link=NULL;
if(*front) (*rear)->link=temp;
else *front = temp;
*rear = temp;
}
element deleteq(queuenode_ptr *front) {
queuenode_ptr temp=*front;
element x;
if(!(*front)) {
fprintf(stderr,"The queue is empty\n");
exit(1);
}
x=temp->item;
*front=temp->link;
free(temp);
return x;
}
int main()
{
queuenode_ptr front=NULL, rear=NULL;
element x; x.key=50;
insertq(&front, &rear, x);
insertq(&front, &rear, x);
insertq(&front, &rear, x);
printf(" Begin Queue Test ...\n");
while(! front==NULL)
{
x = deleteq(&front);
printf("value = %d\n", x.key);
}
}
#define MAX_QUEUES 10
typedef struct queue * queue_ptr;
typedef struct queue{
element item;
queue_ptr link;
};
queue_ptr front, rear;
void insert(queue_ptr *front, queue_ptr *rear, element x){
queue_ptr temp = (queue_ptr)malloc(sizeof(queue));
if(!temp){
fprintf(stderr, "The memory is full\n");
exit(1);
}
temp->item = x;
tmpe->link = NULL;
if(*front)
(*rear)->link = temp;
else
*front = temp;
*rear = temp;
}
element delete(queue_ptr *front){
queue_ptr temp = *front;
element x;
if(!front){
fprintf(stderr, "The queue is empty\n");
exit(1);
}
x = temp->item;
*front = temp->link;
free(temp);
return x;
}<insert>

Case 1
생성된 기억 장소가 n개
front가! NULL이고 rear가! NULL이면
Case 2
생성된 기억 장소가 0개
front가 NULL이고 rear가 NULL이면
1. temp 동적 할당
2. temp의 데이터 값 대입하기
3. temp의 link NULL로 초기화
4-1. front가! NULL이면 rear가 가리키는 곳의 link를 temp에게 준다.
4-2. front가 NULL이며 rear가 가리키는 곳을 temp로, front가 가리키는 곳을 temp로
5. rear가 temp를 가리킨다.
<delete>

1. temp가 삭제될 노드를 가리킨다.
2. x에 삭제될 노드 데이터를 삽입한다.
3. temp의 링크가 가리키는 곳의 값을 front 값으로 바꾼다.
4. 동적 할당 해제
5. return x;
'CS > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ 자료구조 ] O 표기법, 큐, 스택 (4) | 2021.11.02 |
|---|---|
| [ 자료구조 ] 리스트와 연결 리스트 공통점과 차이점 총정리 (6) | 2021.11.01 |
| [ 자료구조 ] linked list 연결 리스트 , k값을 가진 노드 삭제 삽입 함수 (2) | 2021.10.29 |
| [ 자료구조 ] linked list 연결 리스트 반복문으로 node 생성하기 (0) | 2021.10.29 |
| [ 자료구조 ] 단순 연결 리스트 (0) | 2021.10.28 |