[ 자료구조 ] linked list 연결 리스트 반복문으로 node 생성하기
데이터 값이 역순으로 생성되는 경우
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node * link;
};
typedef struct node list_node;
typedef list_node *list_ptr;
int main(){
list_ptr ptr = NULL, before = NULL; int i; // 그 전 노드를 기억하기 위해 before을 사용한다.
for(i = 1; i<= 4; i++){
ptr = (list_ptr)malloc(sizeof(list_node)); //동적할당
ptr->data = i*1; //데이터 값 설정
ptr->link = before; // 첫번째 생성될때는 NULL값이, 반복문이 진행되면 before의 링크가 전달
before = ptr; // ptr의 값을 before에 전달해 다음 link가 가리킬 것을 나타낸다. 연결됨
}
printf("%d \n",ptr->data); // 40 출력
printf("%d \n",ptr->link->data); // 30 출력
printf("%d \n",ptr->link->link->data); // 20 출력
printf("%d \n",ptr->link->link->link->data); //10 출력
for( ; ptr; ptr = ptr->link){ // ptr>0, 즉 참일 때 반복문이 돌아간다.
//for( ;ptr != NULL; ptr = ptr->link)
printf("%d \n", ptr->data); // ptr이 null을 가리키면 반복문을 빠져나온다.
}
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node * link;
};
typedef struct node list_node;
typedef list_node *list_ptr;
int main(){
list_ptr ptr = NULL, befor = NULL; int i; // 그 전 노드를 기억하기 위해 before을 사용한다.
for(i = 1; i <= 4; i++){
ptr = (list_ptr) malloc(sizeof(list_node)); //동적 할당
ptr->data = i*1; //데이터 값 설정
ptr->link = before; // 첫 번째 생성될 때는 NULL값이, 반복문이 진행되면 before의 링크가 전달
before = ptr; // ptr의 값을 before에 전달해 다음 link가 가리킬 것을 나타낸다.
}
printf("% d \n", ptr->data); // 40 출력
printf("% d \n", ptr->link->data); // 30 출력
printf("% d \n", ptr->link->link->data) ; // 20 출력
printf("% d \n", ptr->link->link->link->data); // 10 출력
for( ; ptr ; ptr=ptr->link){ // ptr>0, 즉 참일 때 반복문이 돌아간다.
printf("% d \n", ptr->data); // ptr이 null을 가리키면 반복문을 빠져나온다.
}
}
// 마지막 출력 반복문 ptr = ptr->link
// 원래 ptr이 가리키는 곳을 출력하는 것이라 반복문으로 작성해도 무관하다.
// ptr > 0 -----True
// ptr = 0 (null) -----False
// ptr->link->link->link->link의 값을 NULL이다. 이때 false가 되어 반복문을 빠져나온다.
메모리 생성을 이미지로 형상화 하기
위로 올라가며 생성되고 순환한다.
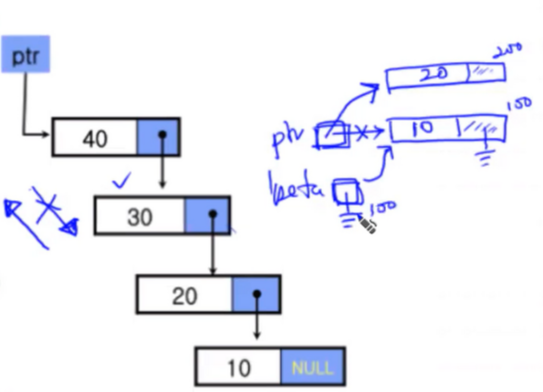
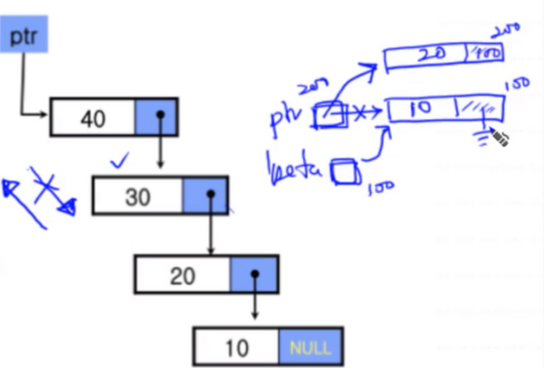
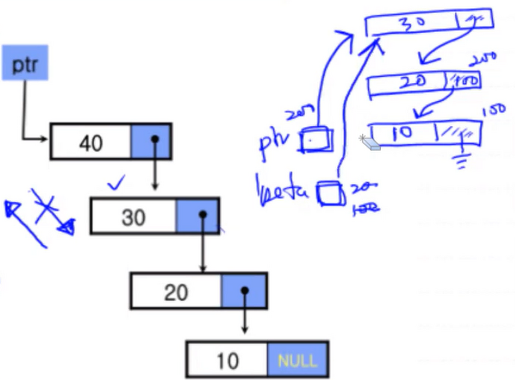
리스트 출력 함수 print_list()
void print_list(list_ptr ptr){ // ptr 첫번째 구조체 포인터를 가져온다.
printf("The list contains : ");
for(; ptr; ptr = ptr->link){
printf("%4d", ptr->data);
printf("\n");
}
}void print_list(list_ptr ptr){ // ptr 첫 번째 구조체 포인터를 가져온다.
printf("The list contains : ");
for(; ptr; ptr = ptr->link){
printf("%4d", ptr->data);
printf("\n");
}
}
데이터 값이 순서대로 생성되는 경우
list_ptr create(int n){ // 들어온 숫자만큼 동적할당하기
list_ptr first, temp = NULL, before = NULL;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
temp = (list_ptr)malloc(sizeof(list_node));
temp->data = (n-i+1)*10; // 위에 코드와 비교했을때 오름차순 정렬로 데이터 할당
temp->link = before;
before = temp;
}
first = temp;
return first;
}list_ptr create(int n){ // 들어온 숫자만큼 동적할당하기
list_ptr first, temp = NULL, before = NULL;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
temp = (list_ptr) malloc(sizeof(list_node));
temp->data = (n-i+1)*10; // 위에 코드와 비교했을 때 오름차순 정렬로 데이터 할당
temp->link = before;
before = temp;
}
first = temp;
return first;
}

완성된 최종 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node * link;
};
typedef struct node list_node;
typedef list_node * list_ptr;
list_ptr create(int n) {
list_ptr first=NULL, temp=NULL;
int i;
for(i=0; i < n; i++)
{
temp = (list_ptr)malloc(sizeof(list_node));
temp->data=rand()%100; /* 리스트의 값 */
temp->link=first; /* 새로운 노드를 리스트의 맨 앞에 삽입한다. */
first = temp;
}
return first;
}
void print_list(list_ptr ptr) {
printf("The list contains: ");
for( ; ptr; ptr = ptr->link)
printf("%4d", ptr->data);
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
list_ptr ptr = NULL;
ptr = create(6); /* 6개의 노드를 가진 연결리스트를 만든다 */
print_list(ptr);
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node * link;
};
typedef struct node list_node;
typedef list_node * list_ptr;
list_ptr create(int n) {
list_ptr first=NULL, temp=NULL;
int i;
for(i=0; i < n; i++)
{
temp = (list_ptr) malloc(sizeof(list_node));
temp->data=rand()%100; /* 리스트의 값 */
temp->link=first; /* 새로운 노드를 리스트의 맨 앞에 삽입한다. */
first = temp;
}
return first;
}
void print_list(list_ptr ptr) {
printf("The list contains: ");
for( ; ptr; ptr = ptr->link)
printf("%4d", ptr->data);
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
list_ptr ptr = NULL;
ptr = create(6); /* 6개의 노드를 가진 연결 리스트를 만든다 */
print_list(ptr);
}
'CS > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ 자료구조 ] linked list 노드 삭제, 연결 리스트를 이용한 스택 큐 구현 (1) | 2021.10.30 |
|---|---|
| [ 자료구조 ] linked list 연결 리스트 , k값을 가진 노드 삭제 삽입 함수 (2) | 2021.10.29 |
| [ 자료구조 ] 단순 연결 리스트 (0) | 2021.10.28 |
| [ 자료구조 ] 연결리스트를 만들기 위한 구조체 선언과 typedef 활용 (1) | 2021.10.27 |
| [ 자료구조 ] 링크드 리스트 Linked List 연결 리스트 동적 기억 장소에서 포인터 사용 (2) | 2021.10.26 |